Radiation
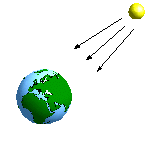
Radiation is a form of energy. Every body emits rays when its temperature is above 0 Kelvin. The temperature has the main influence when transferring heat by radiation. Besides, the ability of a body for absorbing radiation energy depends on the composition of the surface. An ideal white surface will reflect all incomming energy, while an ideal black surfice will absorb it.
The quantity of transfered energy between two bodies is not effected by the distance between themself, if there is no material in between. Gases built up with one or two atoms are permeable for radiation.
The heat emission by radiation is described by the law of Stefan-Bolzmann:
Q = A ∙ ε ∙ σ ∙ T4
A = Surface of the heat transfer [m²]
ε = Emission hight [-]
σ = Stefan-Boltzmann constant factor [5,67 ∙ 10-8 W / m² ∙ K4 ]
T = Temperature of the body [K]
(e.g. The emission hight of steel tube lines is 0,75)
In a steam boiler we find radiation heating surfaces near the combustion.