Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat from a warm molecule to a cooler one. Some materials conduct heat better than others; e.g., gases and vapors are poor conductors, liquids are better, and metals are best.
The quantity of transfered heat depends on the property of the material, the difference in temperature and the measures of the body.
The heat transfer by convection is described by the following equation:
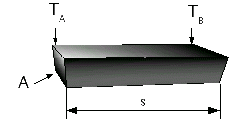
Q = λ ∙ A / s ∙ ( TA - TB )
λ = Coefficient of conductivity [W / ( m ∙ K) ]
A = Area of heat transfer [m²]
s = Width of heat conductor [m]
TA - TB = Difference in temperature between hot and cold side [K]
The conductivity of some material is as follows:
| Material |
Conductivity in W/mK |
| Mild Steel | 48 |
| Stainless steel | 24 |
| Copper | 386 |
| Aluminium | 229 |
| Brick | 0.4 - 0.7 |
| Concrete | 0.8 - 1.4 |
| Wood | 0.1 - 0.2 |
| Cork board | 0.04 |
| Water | 2.2 |
| Air | 0.02 |
| Scale | 0.12 - 0.17 |